How Laparoscopic Surgery is Performed: Step-by-Step Guide
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery (MIS) or keyhole surgery, is performed through small incisions with the help of a camera and specialized instruments. Here’s how the procedure is typically done:
🔹 Step 1: Preparation and Anesthesia
- The patient is given general anesthesia to ensure they are asleep and pain-free during the procedure.
- The abdomen is cleaned and sterilized to reduce the risk of infection.
🔹 Step 2: Creating Access (Port Insertion)
- A small incision (usually near the navel) is made.
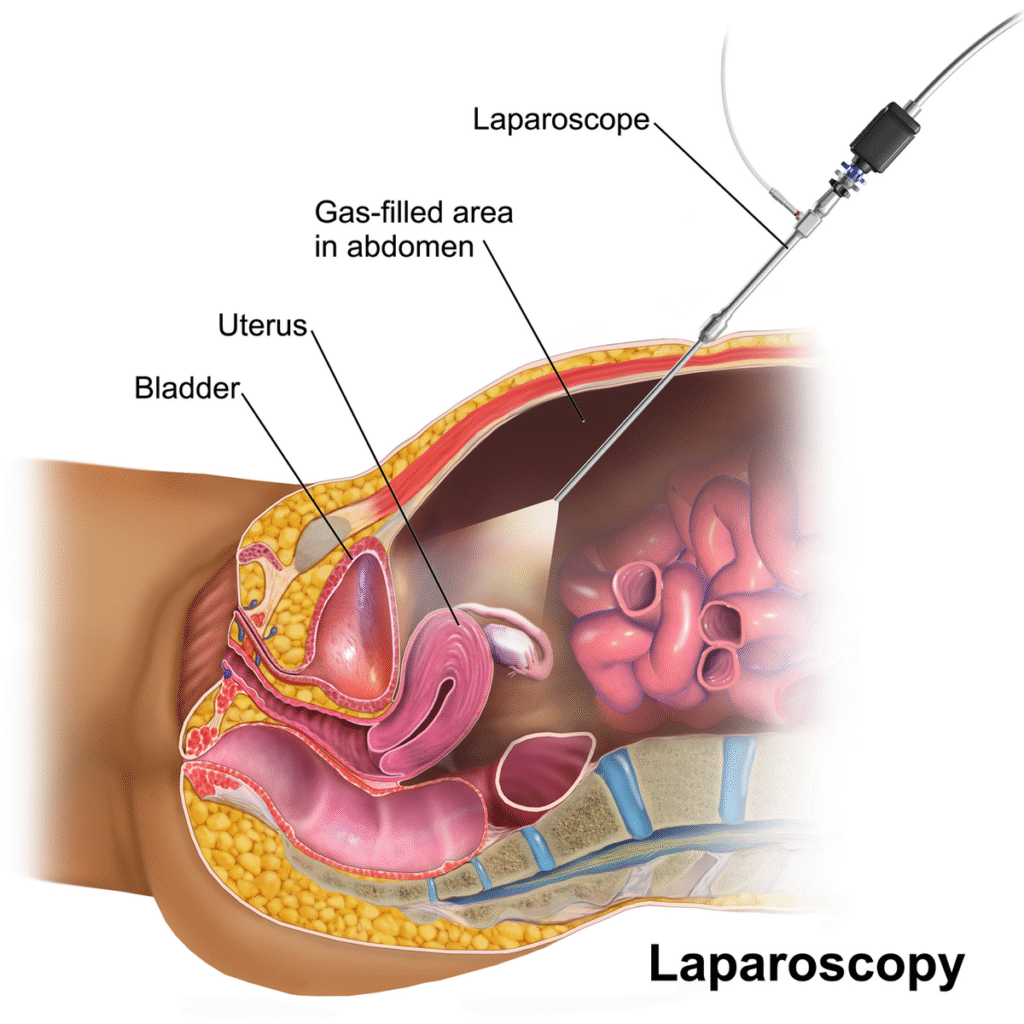
- A Veress needle or similar device is used to inflate the abdomen with carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas. This creates space for the surgeon to see and work.
- A trocar (tube-like instrument) is inserted through this incision.
🔹 Step 3: Inserting the Laparoscope
- A laparoscope (a long, thin tube with a high-resolution camera and light at the end) is inserted through the trocar.
- The camera transmits real-time images to a monitor, giving the surgeon a clear view of the organs.
🔹 Step 4: Making Additional Incisions
- One to three more small incisions are made for inserting specialized surgical instruments (e.g., scissors, graspers, electrocautery).
- The surgeon operates by watching the monitor and manipulating the instruments.
🔹 Step 5: Performing the Surgery
Depending on the reason for surgery, the surgeon may:
- Remove organs (like the gallbladder, appendix, uterus).
- Treat problems like endometriosis, hernia, cysts, or fibroids.
- Take a biopsy or perform repairs.
🔹 Step 6: Closing the Procedure
- After the surgery is completed:
- The instruments and laparoscope are removed.
- The gas is released from the abdomen.
- The small incisions are closed using stitches or surgical tape.
- A bandage is applied to each site.
🔹 Step 7: Recovery
- Patients are monitored in a recovery room.
- Recovery time is generally much faster than open surgery.
- Many patients go home the same day or within 1–2 days.
✅ Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery:
- Smaller incisions, less scarring
- Faster recovery
- Less pain and bleeding
- Lower risk of infection